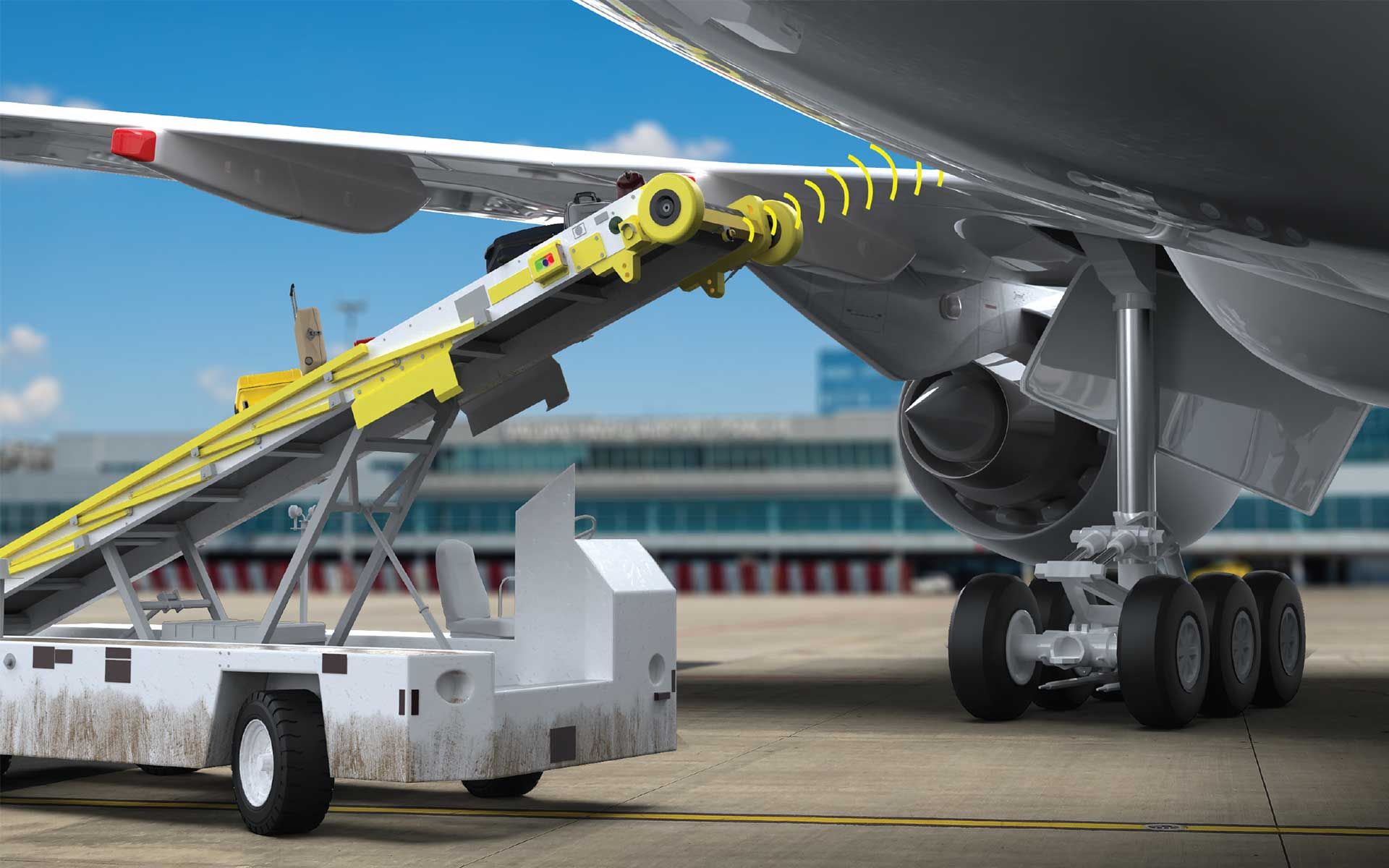
Radar sensing is a wireless sensing technology that discovers and extracts an object's position, shape, motion characteristics, and motion trajectory by analyzing “received” echo characteristics. As demonstrated by bats, radar sensing functions much like human eyes and ears.
Generally speaking, most people outside the industry associate radar technology with aircraft tracking or checking driving speeds. However, the advances in radar sensor technology have produced smaller, less expensive applications widely used in industrial applications and everyday life.
In today’s post, we’re spotlighting radar sensors by Banner Engineering. Specifically, we’ll cover the many benefits of radar sensors and how to choose the right Banner Engineering sensors for numerous applications based on device characteristics and use cases.
Radar Motion Sensor Benefits
A radar sensor is a conversion device that can convert microwave echo signals into electrical signals. These sensors use wireless detecting technology like FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) and PCR (Pulsed Coherent Radar) to detect motion by determining an object’s shape, position, trajectory, and characteristics.
In addition to countless industrial applications, radar sensors, like a Banner distance sensor, are widely used to detect motion and positioning. For example, we encounter radar sensors in cars (i.e., collision detection systems), drive-thru windows, and automatic car washes.
There are many advantages to using Banner radar sensors compared to other sensor types, including the following benefits.
- Works in extreme temperatures, precipitation, dirt, dust, and low light.
- Recognizes both moving and stationary objects.
- Functions equally well indoors and outdoors.
- Suitable for mounting in enclosures.
- Detects objects through plastic or glass, even when opaque or dirty.
- Ability to focus on a primary target while ignoring other objects.
- Suitable for long-range detecting.
- Wide beam radar sensors are not affected by varying shapes and surfaces.
Important Radar Movement Sensor Characteristics to Consider
When selecting a radar sensor for any application, there are important characteristics to consider, including operating frequency, beam pattern, adjustable-field or retroreflective, and configuration.
Operating Frequency
Different radar frequencies (a.k.a., ISM bands) affect not only the range of the sensor but also what materials it can detect. Banner radar sensors are available in 24, 60, and 122 GHz, so let’s review the operating frequencies for each.
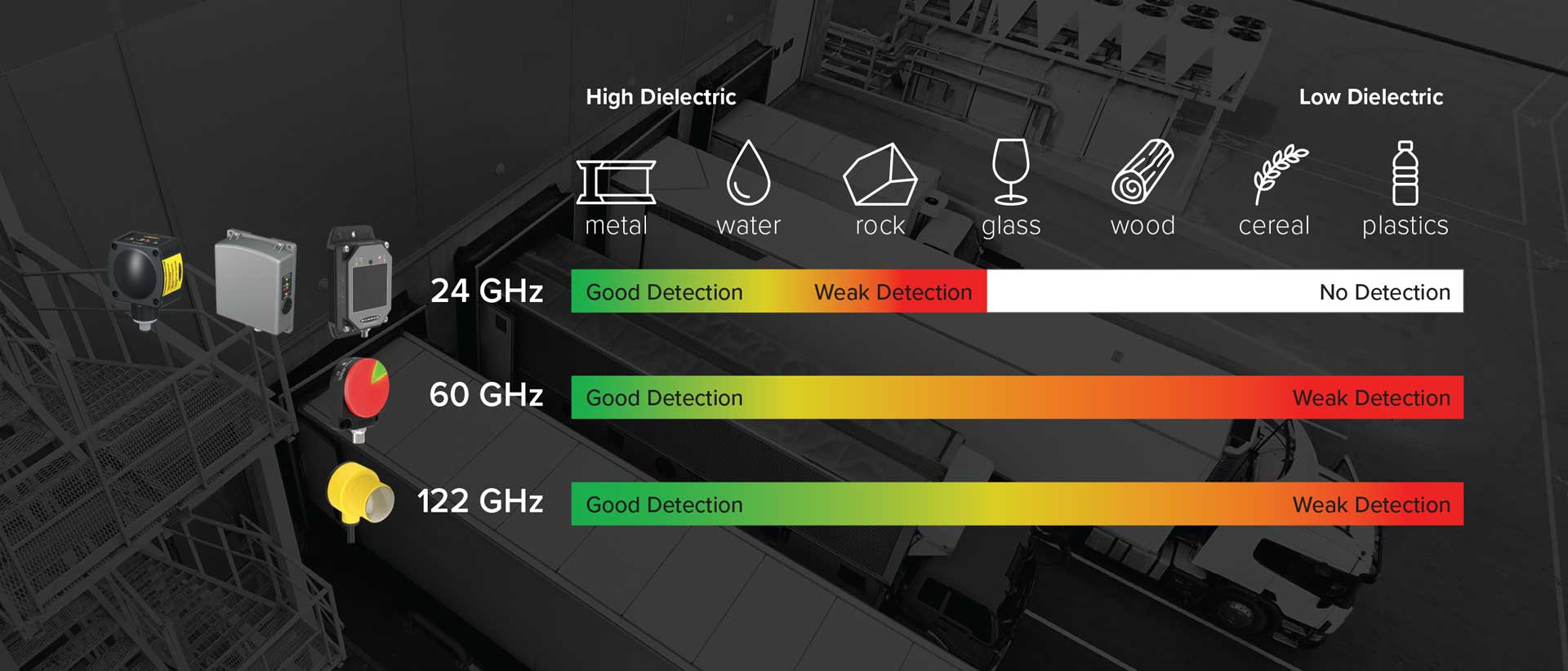

A 24 GHz radar produces long wavelengths and is most useful for detecting large, high-dielectric objects (i.e., metals, water, rock). Alternatively, a 122 GHz radar produces shorter wavelengths, which provides more accuracy and a wider range of detection (i.e., low-dielectric materials like plastic, wood, and other organic materials) than 24 GHz.
Finally, there is the 60 GHz radar that falls between 24 GHz and 122 GHz in terms of performance, with a similar detection range to 122 GHz and better accuracy than 24 GHz.
Beam Pattern
Banner radar sensors are available in narrow and wide beam patterns, which affects detection within coverage areas. For example, a narrow beam pattern focuses on a narrow area for precise object detection, which avoids false detection of objects outside of the region of interest. Radar sensors with a narrow beam pattern are commonly used for drive-thru windows, tank level monitoring, and loading docks.
Alternatively, the Banner proximity sensors with a wider beam pattern can cover larger areas and better detect irregular surfaces and targets at steep angles. Wide beam radar patterns are well-suited for vehicle detection (ex: trains, cars, boats, and toll booths) and collision equipment avoidance.
Adjustable-Field or Retroreflective Sensors
Another important characteristic to consider when selecting the right Banner radar sensor is whether you need an adjustable-field or retroreflective model. The main difference between the two is the reflection method. An adjustable field (diffuse) sensor expects the light to be reflected by the object while retro-reflective sensors expect the light beam to be interrupted by the object to detect it.
An adjustable field radar sensor emits a well-defined beam of high-frequency radio waves from an internal antenna and processes the signal reflected back to the receiving antenna. This type of sensor is ideal for detecting vehicles on roads and near intersections, boat detection for locks and dams, proximity detection for large shipyard cranes and cargo, car counting for parking ramps, gates, and drive-thrus, and subway and light rail logistics.
Like the adjustable field model, the retroreflective model emits a beam of high-frequency radio waves. However, it also requires a dedicated retroreflector to function, like a wall or floor. This allows the sensor to ignore objects in the background beyond the retroreflective target, creating a more focused sensor. Also, retroreflective models can sense targets up to the face of the sensor, which eliminates sensor “dead zones''. Applications for this model include toll booths, gate control, parking ramps, train detection, shipyard logistics, and truck trailer detection at loading docks.
Configuration
Different applications will require different radar sensor configurations that affect the setup, operation, and control of the sensor. For example, if you need to read or change the sensor remotely, there are specific configurations to consider. Following is an explanation of the different configuration options for Banner radar sensors:
- DIP Switch Configuration: easy manual setup.
- GUI Configuration: tamper-proof and provides a clear visual of the entire sensor view for setup and troubleshooting.
- Remote Teach: allows remote configuration of a sensor without manual interaction.
- IO Link: allows you to read and change the sensor remotely and dynamically change parameters.
- Push Button: simple “click and teach” configuration using manual push button.
Different Uses of Movement and Motion Sensor Radars
Radar sensors provide powerful motion detection technology built on the well-established concept of radar. Let’s look at some real-world applications using Banner radar sensors, including the applicable characteristics for each scenario.
Vehicle Detection
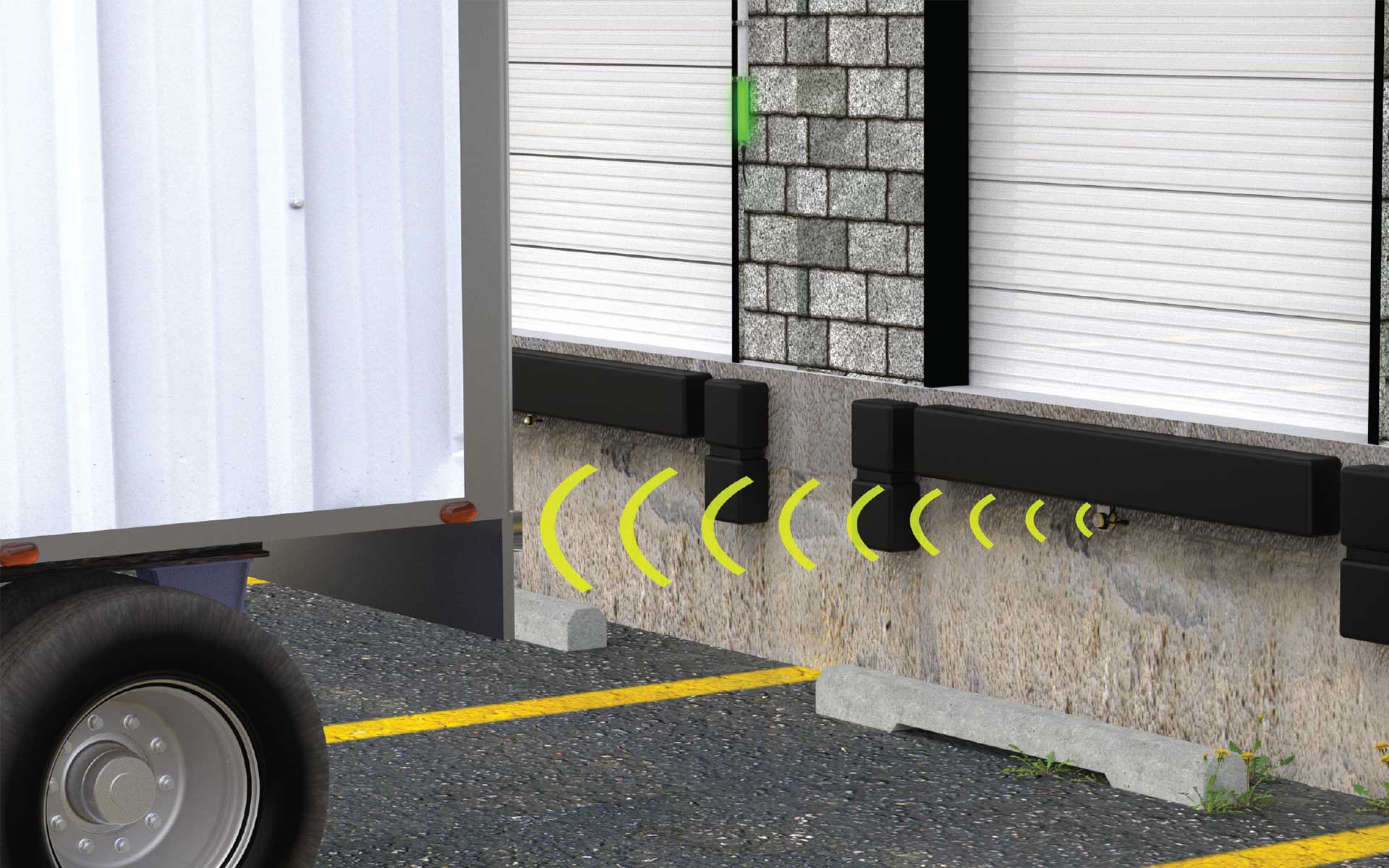


Vehicle detection may be one of the most well-known uses of radar sensors in the modern world. Modern radar sensors using Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) technology reliably detect targets, like cars or trains, in extreme weather conditions. From drive-thru windows to loading docks to automatic car washes, vehicle detection using radar sensors ensures safety and continuity within the operating environment.
Tank-Level Monitoring
Storage tanks, totes, and containers are common in industrial applications. However, properly monitoring and managing levels inside the tank is only possible with visual access to the contents, which is difficult with plastic or metal tanks. However, a radar sensor’s high-frequency radio wave signals can easily penetrate the container’s opaque surface to measure the liquid’s levels, ensuring safety and optimal operation.
Positioning Feedback
Precise positioning of industrial equipment is essential to prevent damage and reduce downtime when visibility is difficult. For example, large ports depend on moving shipping containers quickly and safely for optimal production. However, visibility is often impaired by equipment, weather conditions, and more. In these cases, a 122 GHz radar sensor provides the accurate measurements necessary to quickly detect obstructions and prevent damage during container movement.
Collision Avoidance
Crane operation in enclosed spaces can be challenging, especially in dusty and harsh environments. Fortunately, reliable obstruction detection using a Banner photoelectric sensor with a narrow beam pattern can help these machines avoid the roof and other obstacles in the enclosed space.
How to Choose the Right Radar Sensor for Your Needs?
The versatility and reliability of radar sensors have made these devices invaluable to applications that depend on reliable detection for safety, security, and operational continuity. Banner Engineering’s wide variety of industrial sensors using radar technology provide reliable solutions in applications of all kinds.
Not sure how to choose a sensor for an application? The graph below by Banner Engineering provides excellent guidance for radar selection based on the application’s needs.
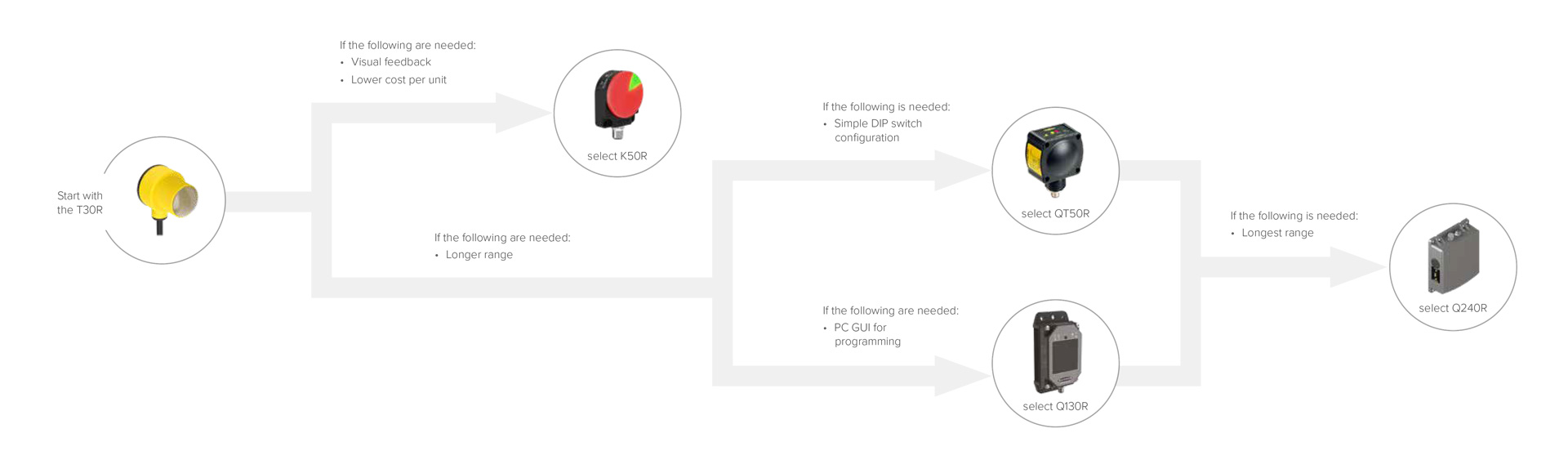

Banner Engineering radar sensors are widely used to solve challenging problems and achieve automation goals around the world, and Peerless Electronics is proud to be an authorized distributor of Banner’s reliable radar sensors. Whether you are shopping for a highly effective Banner laser sensor with an adjustable field or have questions about Banner sensors in our extensive catalog of products, Peerless Electronics can help.




