Electricity powers our society in countless ways. We rely on it for everything from running water used for drinking and washing to streaming shows on our smart TVs and other devices - not to mention keeping the lights on. Given the power electricity provides to run just about every modern amenity available, protecting electricity’s critical power-generating equipment is imperative to both safety and operational success.
Today’s post offers a comprehensive guide to electrical enclosures, including the various types, the significance of enclosure ratings and construction materials, and how to choose the proper electrical cabinets or enclosures for different industrial applications.
What Are Electrical Enclosures?
Let’s begin with the basics: what are enclosures? Electrical cabinets or enclosure boxes are specially designed and tested cases engineered to protect individuals from accidental contact with current-carrying electrical equipment while also protecting the sensitive electrical components from exposure to damaging elements.
There are many types of electrical boxes or enclosures, each specifically designed to protect various applications. Therefore, the following section will review the many types of electrical cabinets available, including common characteristics and associated applications.
Electrical Enclosure Types
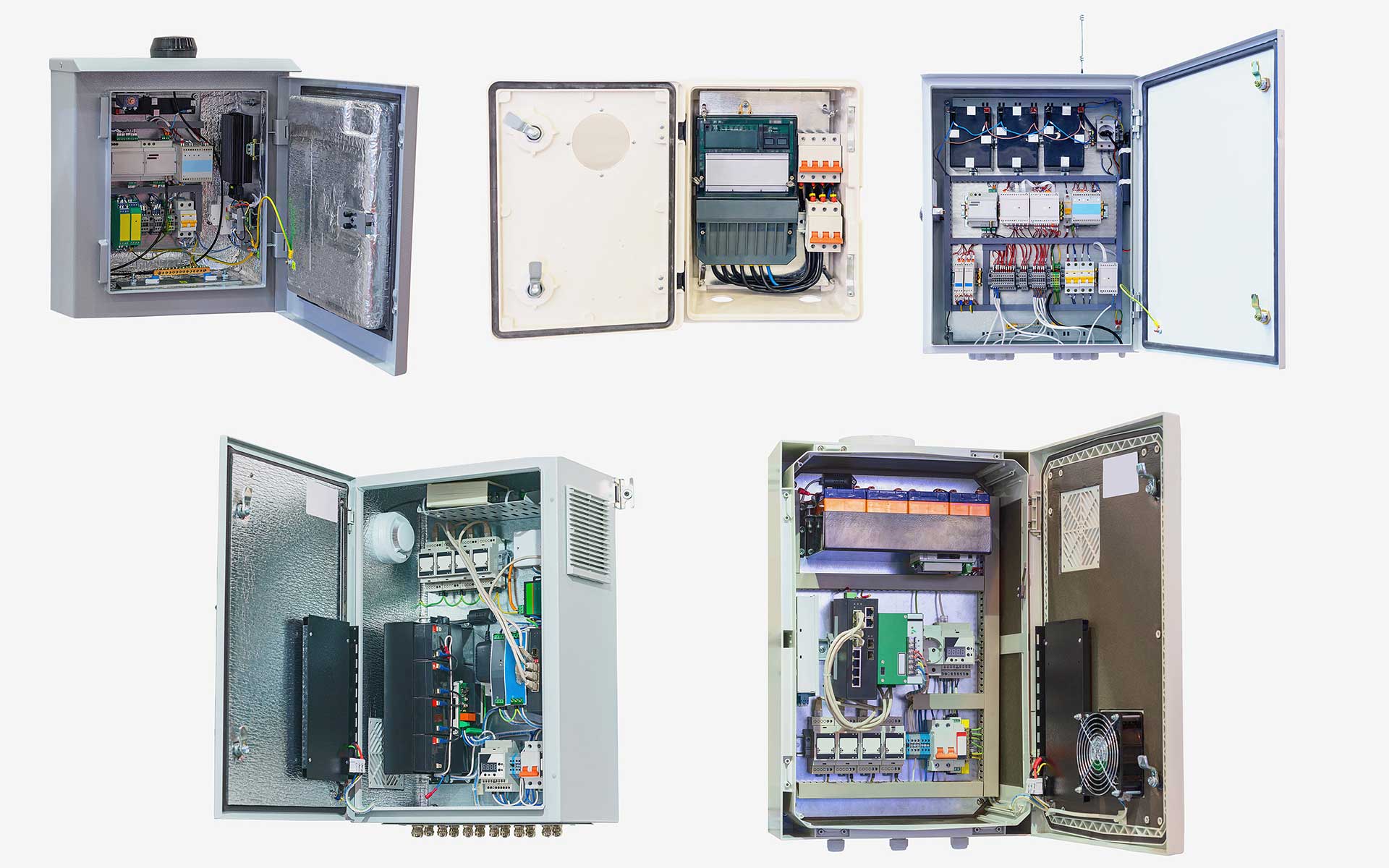


Electrical enclosures can be found in businesses, homes, and public use areas - basically, anywhere electricity is needed to power equipment. However, not all electrical applications are the same, with each enclosure type designed to offer the level of protection electrical application needs.
Wall-mount Enclosures
Wall mount electrical enclosures are the most basic type of enclosure available, and they are suitable for small, low-power applications. These enclosure cabinets are easy to install and can be mounted directly to a wall or another piece of equipment.
Floor-mount & Freestanding Enclosures
Floor-mount and freestanding enclosure types are larger than wall-mounted cabinets and typically used for more complex applications. These electrical enclosures are commonly used indoors and fitted with a variety of accessories, including shelves, drawers, and doors.
Junction Boxes
This type of electrical enclosure is commonly used to protect one or more wiring connections and designed for use as surface-mounted junction boxes, service boxes, switch boxes and cutout boxes. These boxes commonly include pre-punched knockouts for easier cable entry.
Pushbutton Enclosures
Pushbutton enclosures come in various sizes and construction materials, and they are designed with precut standard 22.5mm or 30.5mm opening holes in the cover to allow easy installation and safe access to push buttons, switches, and indicating lights. They are also available with blank covers (with no holes) for complete customization.
Disconnect Enclosures
Disconnect electrical enclosures are designed to allow the addition of a flange-mounted disconnect when necessary, and they are compatible with disconnects and operating mechanisms from various manufacturers. They are typically available in wall-mount, floor mount, and freestanding options.
Consoles & Consolets
Consoles and consolets are heavy duty constructed enclosures that protect contents from contaminating elements and are available in various types, such as freestanding consoles, operator consoles, console tops, or push button consolets. They typically include HMIs, pushbuttons, switches, and other pilot devices and controls where operators can access the devices to control and operate machinery and systems.
Wire Through Enclosures
This type is similar to the junction boxes and efficiently protects short, straight runs of wire and cable from the elements. They typically feature a continuous hinged top for smooth pivotal action and optimal axial rotation.
Sloped Top Enclosures
As the name indicates, the sloped top electrical enclosure boxes feature a 20° slope on the top portion of the enclosure and door flanges to help prevent the accumulation of water and debris on top of the enclosure.
Windowed & Clear Cover Enclosures
Aptly named, these enclosures have a window or clear cover for visibility inside the enclosure without having to open the door and expose the internal components to the operators or outside elements.
Dual Access Enclosures
Dual access enclosures are designed to provide additional access from both the front and the rear side of the enclosure, which can be especially useful in industrial applications.
Flush-Mount Enclosures
Flush-mount electrical enclosures are wall-mounted with an external frame that allows it to be recessed in the wall. These enclosures are ideal in high traffic areas or with applications where external space is limited.
Electrical Enclosure Standards


Electrical enclosure ratings are systems that specify guidelines regarding what applications a particular product is suitable for, and there are several entities that determine electrical enclosure standards. However, each entity creates its own standards when rating electrical enclosures and usually consider at least two primary types of protection in order to rate these products.
There are three primary organizations responsible for the ratings and standards of electrical enclosures in the U.S., which are NEMA, IP, and UL. Keep reading to learn more about each of these organizations and why they are important.
NEMA Enclosure Ratings
NEMA, a.k.a., the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, is an ANSI-accredited trade association that sets standards for electrical equipment (i.e., the NEMA 250 standard) and one of the most widely recognized electrical enclosures rating organizations in the U.S. The NEMA enclosure rating guide is designed to give a recommendation of where electrical panels and systems can be safely used and what environments may suit them.
NEMA panel ratings are graded by a number that can also be followed by a letter in some cases. The NEMA panel ratings begin with NEMA level 1 on up to NEMA level 13, and each number indicates a different level of protection, such as protecting against dust ingress, water ingress, or both in some cases. Therefore, the NEMA panel ratings required for a specific application will depend on a number of environmental factors.
Let’s look at some examples of the NEMA enclosure rating guide and what they indicate for an application, like NEMA 1, 4, and 12 ratings. First, the NEMA 1 enclosure definition includes electrical enclosures suitable for indoor use to protect against unintended contact with the enclosed equipment. However, a NEMA 1 rating enclosure does not provide any protection from water or any other substances, which is why it’s the lowest rating available.
Next up are NEMA 4 and NEMA 12 ratings, which are both known for their durability and ability to provide good protection against the ingress of water and intrusion of solid objects. The most common applications for both are SPEP industrial hardware, such as quarter-turn latches and oil hole seals. However, the NEMA 4 enclosure definition is intended for outdoor use by providing better sealing and resistance against ice formation on the enclosure, whereas the NEMA 12 enclosure definition typically applies to indoor use.
IP Enclosure Ratings
IP enclosure ratings, a.k.a. Ingress Protection enclosure ratings, are standards created by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). IP ratings are relatively straightforward and include the letters “IP” followed by two digits. The first digit indicates what level of protection the enclosure provides against solid objects and particles like dust. The second digit indicates how well the enclosure protects against water or moisture.
Like the NEMA enclosure rating guide, higher numbers in the IP rating system represent a higher level of protection for the electrical enclosures. Within this system, the first digit ranges from 0 to 6, and the second digit ranges from 0 to 9. Therefore, electrical enclosures with a first digit of 5 or higher offer protection against dust particles, and enclosures with a second digit of 7 or higher offer protection against water immersion.
UL Standards for Electrical Enclosures
UL stands for Underwriters Laboratories, which is an independent product safety testing and certification agency that addresses hundreds of different industries worldwide. The UL standards for electrical enclosures are UL50 and UL50E, which are basically equivalent to the NEMA 250 standards, including the same numbering scheme and correlating definitions with only a few minor differences.
However, UL enclosures, like any UL-rated product, are actually thoroughly tested and certified by an independent third-party prior to market release, which often translates to a higher level of trust and confidence in any UL listed enclosure. However, this testing and certification process can be quite costly and time-consuming, which becomes an obstacle for many companies planning new product releases or trying to change suppliers on existing sub-components.
These electrical enclosure rating systems are important and instrumental in guiding selection of the right enclosures for electrical applications, which can help protect the components within while reducing the risk of injury to individuals working around any enclosure type.
Electrical Enclosure Construction Materials

Electrical cabinets also come in various materials that can considerably affect their role and performance. These metallic and non-metallic materials provide many benefits, from quick and easy installation to high resistance to corrosive conditions.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel constructed enclosures are the most cost-effective choice for indoor applications, making them common in many industries. Carbon steel, also commonly called low carbon or mild steel, are not very corrosive-resistant, so most manufacturers will prime and paint the enclosures with a high-quality powder paint for additional scratch-resistance. However, if the carbon steel painted enclosure becomes scratched, it should be repaired immediately with touch up paint to ensure the enclosure maintains corrosion protection.
304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is an alloy that contains an iron base with approximately 18% to 20% chromium to provide corrosion resistance from corrosive solvents, alkalis, and some acids. This makes 304 stainless steel electrical cabinets deal for applications requiring wash-downs with caustic cleaners and both indoor or outdoor applications.
316 Stainless Steel
This type of stainless steel contains molybdenum, which provides additional resistance to corrosion beyond 304 stainless steel, including sea water, chlorine sulfates, bromides, other acids, and high temperatures. This type of steel electrical enclosure is ideal for indoor and outdoor use in applications used by the pharmaceutical, food/beverage, marine, and other industries associated with these circumstances.
316L Stainless Steel
316L stainless steel has a lower carbon content than standard 316 stainless steel, which offers more resistance to corrosion from welding and other activities subject to exposure to temperatures over 425 ºC. Therefore, 316L stainless steel performs better in highly corrosive or temperate circumstances, like those commonly associated with construction.
Aluminum
These enclosures are lighter and more economical than other metallic enclosures, making them ideal for solar, telecommunications, traffic control, wastewater, and other applications where high-heat and corrosive conditions are common.
Fiberglass Reinforced Polyester
Also commonly called fiberglass or FRP enclosures, these non-metallic, lightweight enclosures are easy to install and modify when drilling is required. However, it's important to ensure all openings are properly sealed to maintain the NEMA rating of the enclosure when modifications are made.
FRP enclosures are considered strong enough to resist normal impacts and can resist corrosive environments, such as installations near high-temperature conditions. Some FRP enclosures are also designed to maintain the required protection while temporarily submerged in water.
Polycarbonate
These non-metallic enclosures are made from thermoplastic polymers and deliver a higher degree of impact and UV resistance than other non-metallic enclosures. Polycarbonate enclosures feature cleaner holes and cutouts, eliminating the need for sanding or finishing and making installations and modifications easier. These enclosures are weather resistant and available with clear covers or windows for viewing contents without opening, making them ideal for sensitive equipment.
PVC
Similar to polycarbonate options, PVC enclosures are highly UV and impact resistant, as well as non-conductive. They are available with clear covers or windows for viewing contents without opening and ideal for housing small junction circuits, cabling, and applications requiring watertight and dust-tight seals.
Thermoplastic ABS
Thermoplastic ABS (commonly referred to as simply “ABS”) enclosures offer a high degree of impact, heat, and corrosion resistance, making them ideally suited for FDA controlled food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and medical applications. These non-conductive enclosures are also commonly used for communications panels and wireless equipment such as WiFi, Bluetooth, and radio frequency technologies.
The holes and cutouts are cleaner on ABS enclosures and require no sanding or finishing, making installation and modifications easier, and they are available with clear covers or windows for viewing contents without opening. ABS enclosures are also fully recyclable after use.
Additional Enclosure Accessories
There are also a wide range of accessories for enclosures that can make installations more efficient and enable any feature necessary for the application. Some of the most common accessories utilized in electrical applications include DIN rails, barriers, rack mounts, terminal block strips, brackets, and straps. Other helpful accessories that can help fully customize your electrical enclosure application are alternative mounting and accessibility kits and cable management systems and components.
How to Choose the Enclosure That Fits Your Needs


There are many factors to consider when selecting the right enclosures for electrical applications, including the environment, space, exposure, security, and future modifications. Examining these various factors will help ensure that the enclosure provides safe, efficient, and reliable service. Common considerations in electrical enclosure selection include the following aspects.
Enclosure Size
The size of the components and devices to be housed will help determine the size of enclosure needed for the application. This includes wire duct, terminal blocks, space for routing wires, etc. Also, remember to allow space for subpanel mounting holes, cable entry, protrusions for externally-mounted items, and any possible future additions. The device manufacturer should specify any space requirements or tolerances necessary.
Enclosure Type
The enclosure type should best serve the application’s conditions.Therefore, it’s critical to know and understand all the variables that will affect the enclosure, such as the enclosure location, service provided, and type of mounting necessary.
Enclosure Material
The enclosure material will depend on the same variables as above, i.e., location, use, and mounting specifications.
Enclosure Protection Rating
As explained in the earlier sections about standards and ratings, these same variables will also help determine the protection rating necessary to withstand the application’s environment.
Security Requirements
Depending on the operation/application, the enclosure may require additional protection against unauthorized access to internal components. Manufacturers offer many options for enclosure security, such as a screw cover, lift-off cover, or single door with clamps for low-risk installations. Higher risk applications may require enclosures with locking capabilities to restrict access to authorized personnel.
Accessories
The electrical enclosure installation location, environment, and service function will typically drive the selection of any accessories that will help with installation and efficient operation.
Shop Fibox
Peerless Electronics is an authorized distributor of a wide range of electrical enclosures by Fibox! Easily and securely shop our entire line of top-quality electrical enclosures.
Plus, our entire product line is backed by over 50 Value Added Services, including custom tailored technical support and expert guidance.






























































































