Electric vehicles are more popular today than ever for various reasons, including heightened emission concerns, rising gas prices, and increased mainstream availability. Several types of electric vehicles are available for personal and commercial use, and we’re exploring each one - from functionality to components - in addition to topline information about the major electric car components most commonly found in every type of EV.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are three main types of electric vehicles available to consumers today - battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), and hybrid electric vehicles (HEV), as shown in the electric vehicle diagram below.
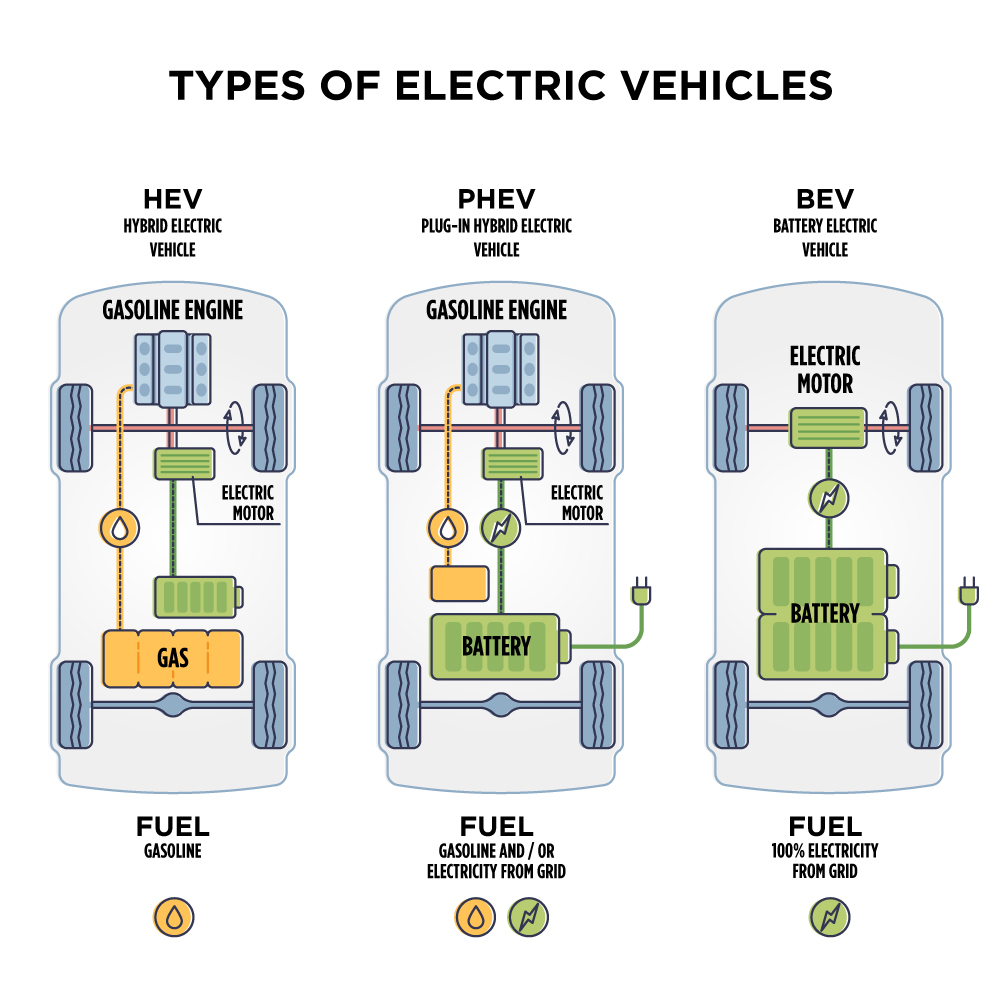

Although they all use electricity to improve vehicle efficiency, each type differs slightly in advanced features. Let’s explore the main differences between each vehicle's electric functionality and performance.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
These types of electric cars or vehicles utilize a battery to function, eliminating the need for gasoline. All plug-in electric vehicles of this type are charged by physically plugging into electric charging equipment. BEV electric vehicles always operate in all-electric mode, i.e., from the battery charge, and have typical driving ranges from 150 to 400 miles.
Plug-in electric cars, such as Tesla models, have become quite popular in recent years. In the commercial sector, there has also been a recent rise in plug-in electric vans - especially with companies that provide delivery services (such as Amazon).
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV) are powered by both an internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor - hence the term hybrid. With these vehicles, batteries power the electric motor, and another fuel, typically gasoline, powers the internal combustion engine.
The batteries in PHEVs can charge through charging equipment or regenerative braking, and they are generally larger than other hybrid electric vehicles' battery packs. This larger battery makes it possible to drive moderate distances using just electricity (about 15-60+ miles), which is commonly referred to as the "electric range" of the vehicle.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV)
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is powered by an internal combustion engine (ICE) and one or more electric motors, which use energy stored in batteries. Rather than plugging in, the battery in an HEV charges through the internal combustion engine and regenerative braking.
The benefit of the extra power provided by the electric motor is a smaller engine. Also, the battery can power auxiliary loads and reduce engine idling when stopped, which results in better fuel economy without sacrificing performance. One of the more famous examples of an HEV is the Toyota Prius.
Electric Vehicle Parts List
Despite the differences in these three types of electric vehicles, each requires the same major components to function. What are the main components of electric vehicles - car type withstanding? As this electric motor parts diagram illustrates, the major major components in all environmentally friendly electric vehicles differs from their gasoline counterparts.


Keep reading for a topline explanation of each main component’s primary function within the vehicle operating system, which helps explain how electric vehicles work.
Electric Traction Motor
Every electric car has an electric motor, i.e., machines that convert electrical energy from stored power or a direct electrical connection into mechanical energy through the production of rotational force. Electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines because they convert over 85 percent of electrical energy into mechanical energy, or motion, compared to less than 40 percent for a gas combustion engine. They are also smaller, lighter, and cheaper.
The electric traction motor is an electric engine that uses power from the traction battery pack to drive the vehicle's wheels and is one of the major components of electric vehicles. There are two types of electric motors widely used in electric cars to provide power to the wheels, direct current (DC) motors and alternating current (AC) motors, which are detailed next.
DC Motors
DC Motors are powered by direct current and can run on anything between 96 to 192 volts. DC motors are further classified into brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors (BLDC), and permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM). Electric vehicle manufacturers typically use a brushed DC motor because these motors are easy to install and less expensive than AC motors.
AC Motors
The AC motor is an alternating current motor or three-phase motor that is powered by 240 volts of alternating current and includes two categories: induction motor and synchronous motor. The induction motor is more cost-effective, thanks to lower maintenance and better reliability, and is widely used by high-performance electric vehicles like the Tesla Model 3.
Auxiliary Battery
Electric car batteries are the vehicle's life force. The auxiliary battery is the low-voltage battery that provides electricity to start the car before the traction battery is engaged. It also powers the vehicle’s accessories.
Charge Port


The charge port is the equivalent of the gas tank opening on an internal combustion engine vehicle. However, instead of adding gasoline, the charge port is where the vehicle plugs into a power source to charge the battery.
DC/DC Converter
This part of an electric vehicle converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run the vehicle’s accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Onboard Charger
Most electric cars have an onboard charger, which is used for standard AC charging, and they limit the total amount of power entering the battery to avoid any electric damage.
Power Electronics Controller
The power electronic controller controls the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces by managing the flow of electrical charge delivered by the traction battery.
Thermal Cooling System
The thermal cooling system manages the operating temperature of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components in electric cars.
Traction Battery Pack
The traction battery pack stores electricity for use by the electric motor.
Electric Transmission
The electric transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric motor to drive the wheels. Electric cars use a single-speed transmission because the motor is efficient in a wide range of conditions.
The desire to drive more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles are fueling the popularity of electric vehicles for personal and commercial use, increasing the demand for the electrical parts required to make and maintain the growing EV market.
As one of the world’s leading authorized stocking distributors of products in this space, Peerless Electronics is a proud carrier of top-tier manufacturers like Honeywell, Sensata, Safran, TE Connectivity, ETA, and P-Duke. Conveniently shop our extensive online inventory today!
Questions about items on your EV parts list?
Contact us today for answers!




