The safety of wire connections in industrial applications is paramount. They ensure reliable operation, protect equipment, and prevent accidents or electrical hazards. Many methods exist for connecting wires, from soldering to splicing. However, these methods are less efficient in high-demand environments or large-scale wiring systems. Enter the terminal block, an effective solution when ease of installation, secure connections, modularity, scalability, and safety are priorities. Today, we’re answering the basic question of what is a terminal block while exploring this solution’s different types by connection, mounting, application, and what to consider when choosing a terminal block.
What Is a Terminal Block?
Terminal blocks are modular, insulated wire connectors that come in various types to suit different electrical applications, including screw-type, spring clamp, and push-in types. All terminal blocks, regardless of type, consist of three primary components: an insulation body, a current-carrying bar, and a clamping mechanism. The insulation body is typically composed of high-strength, heat-resistant, and non-conductive materials like thermoplastics or thermosetting resins. The current carrying bar consists of highly conductive metals, e.g., copper, brass, or alloys, offering an electrical path between wires while ensuring minimal resistance and heat generation during current flow. The clamping mechanism safely secures the wiring to the current-carrying bar to provide a stable, low-resistance connection within the terminal, preventing wires from loosening due to vibrations or mechanical stress.
In industrial electronic applications, terminal blocks offer a reliable, organized, and safe wiring solution that easily scales with system growth. Furthermore, their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with various components make them ideal for power, signal, and data connections in demanding environments. Next, we’ll explore various types by function and connection methods, as well as common mounting styles.
Types of Terminal Blocks by Function
There are times when a terminal block connection needs to serve a specific functionality, like grounding or adding overcurrent protection in series. Following are a few of the more common terminal blocks used in industrial electronics to meet a specific need in the function of the application.
Ground Terminal Block
These terminal blocks are specifically designed for grounding or earthing electrical systems, where the terminal connects to the ground rather than wire to wire. A ground terminal block ensures electrical safety and reliability through a secure ground connection.
Fuse Terminal Block
A fuse terminal block replaces the metal bar with a fuse, which is placed in series when the wires connect to it. This eliminates the need for external fuses, making it the best solution for applications that require fuse protection or circuit protection in the same location as the connection.
Thermocouple Terminal Block
These terminal blocks are specially designed for connecting thermocouples to control systems for accurate temperature measurement, as thermocouple lead connections aren’t compatible with typical terminal clocks. With this in mind, these terminal blocks are designed to minimize the creation of any additional thermal EMF (i.e., electrical voltage caused by temperature differences) between the wires and the terminals.
Types of Terminal Blocks by Connection Method
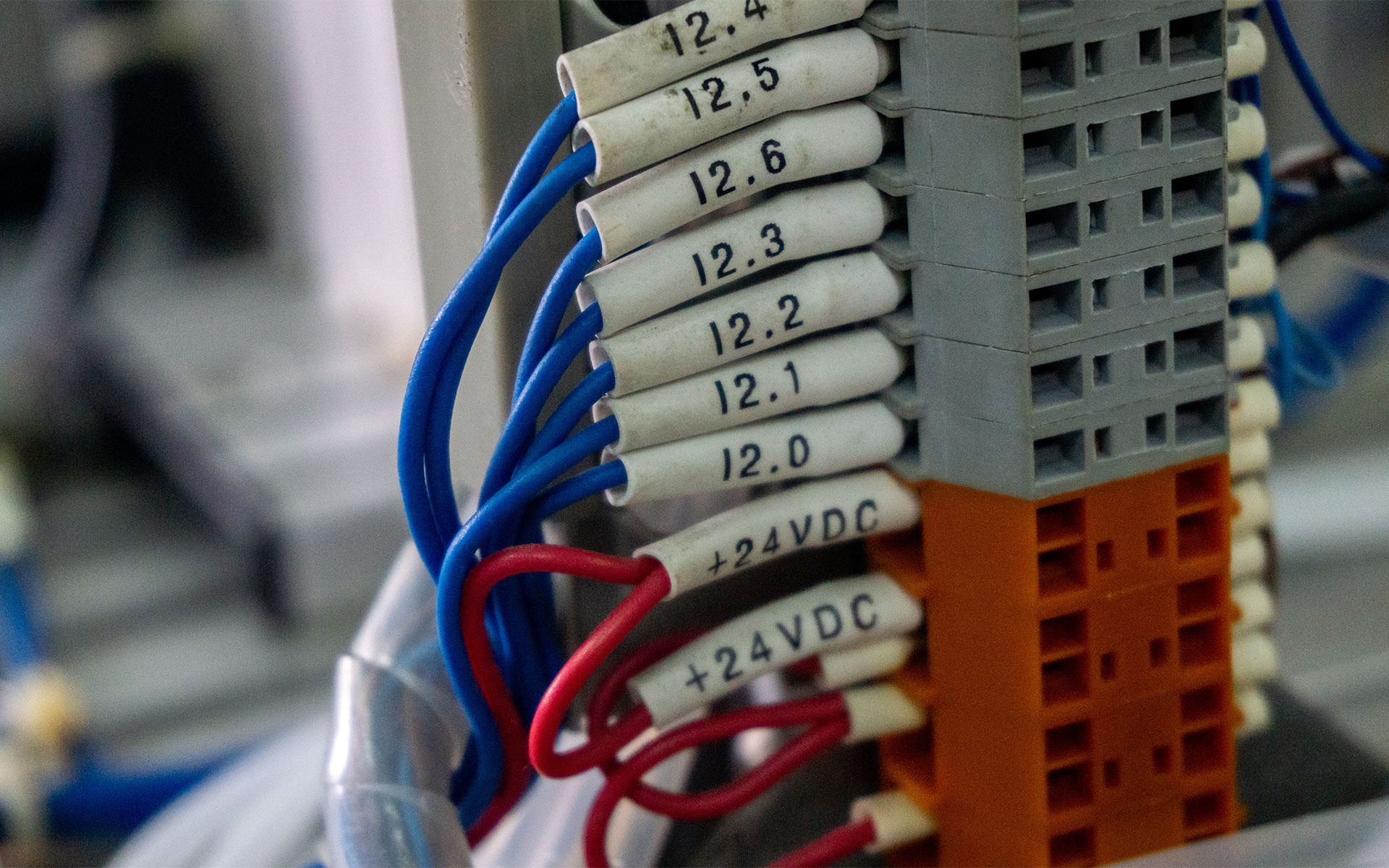


Terminal block connectors offer various methods of connecting wires within an application. Options include screw-type, spring-clamp, push-in, and other mechanisms. Each serves specific needs based on installation speed, reliability, and the type of connection required.
Screw-Type
Likely the most well-known in the field, this type uses screws to clamp wires securely within terminal block connectors. However, use caution when screwing the wires in, as overtightening can damage the wires.
Spring-Clamp/Spring-Loaded
Screwless connections are gaining popularity. This type utilizes a spring mechanism (i.e., spring pressure) to clamp and secure the wire rather than screws. Spring-clamp terminal blocks often require attaching a ferrule to the wire before inserting. The ferrule or wire is then attached and released by inserting a spring release tool, which, depending on the manufacturer, can be a unique spring-release device or a small screwdriver.
Push-In
A push-in connection allows wires to be directly inserted and held in place. Like the spring clamp, most push-in terminals require a ferrule, which strengthens the wire's end and ensures a secure connection. Unlike the spring-clamp version, it features a release device mounted right next to the wire insertion point.
IDC (Insulation Displacement Connection)
IDC (insulation displacement connection) technology is among the newest and fastest screw-less connection types. This version uniquely features two sharp blades inside the terminal block, which slice through the insulation and contact the wire. This type eliminates the need to strip insulation before connecting.
Barrier
What is a barrier terminal block? Featuring a robust construction with insulating barriers that separate each connection point to prevent accidental short circuits, they are larger and bulkier than other types, with screws used to securely terminate wires. Their design accommodates a wide range of wire sizes, providing stable, high-current connections and ensuring durability in demanding environments such as power distribution.
Stud-Type
These terminal blocks securely connect wires using lugs and bolts, creating a mechanically strong bond that resists loosening due to vibration or mechanical stress. They are well-suited for industrial environments where equipment may experience movement or temperature fluctuations.
Pluggable
The pluggable terminal block features a plug-and-socket configuration. The plug section connects to the wires, while the socket mounts onto a DIN rail or PCB. These types are ideal for applications requiring frequent maintenance or modular system designs.
Mounting Styles for Terminal Blocks
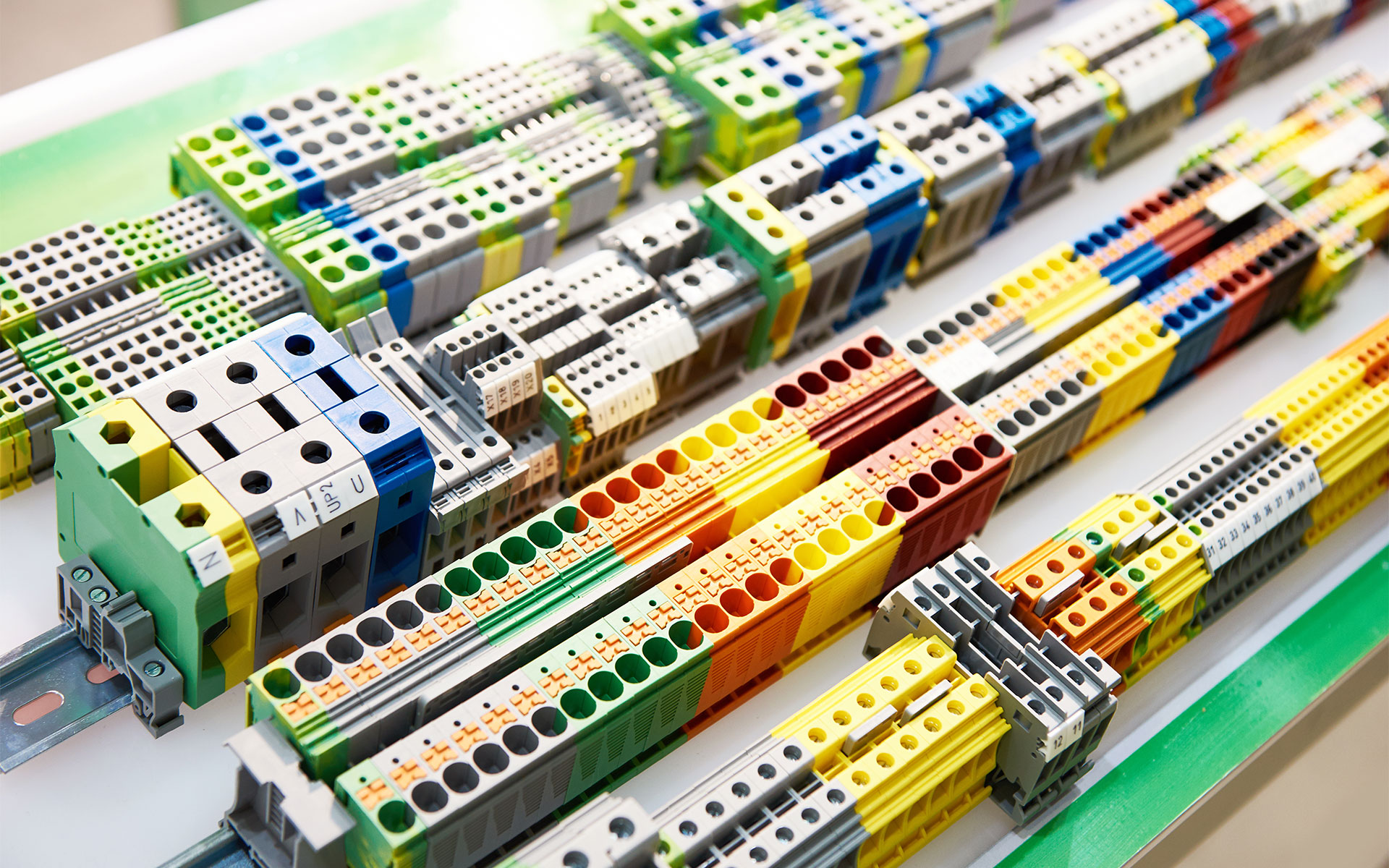

Terminal blocks can also be categorized by mounting styles, which determines how they are installed within a system. The most common mounting solution for terminals is DIN rail, as it tends to simplify wiring setup, making it easy to install and remove the terminal blocks while saving space in the panel or cabinet. Another popular option in industrial applications is panel mounting, where the terminal blocks are secured directly to a panel or enclosure using screws or bolts. This mounting style is strong and secure, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Applications of Terminal Blocks in Industrial Automation
What is a terminal block used for? In industrial automation, terminal block connectors play a critical role in power distribution and signal transmission. They ensure safe and organized wiring in systems where reliability is essential. For power distribution applications, they safely connect wires, distributing power from the main source to motors, controllers, drives, and other equipment within the system. For signal transmission, terminal blocks securely connect low-voltage or analog signals, preserving signal integrity and ensuring precise communication between sensors, controllers, and actuators.
Factors to Consider When Choosing A Terminal Block
Given the many types of terminal blocks available, several factors must be considered when choosing the most appropriate option for a given application.
- Current Requirements: Terminal blocks are designed to handle specific current ratings, and exceeding the threshold can cause overheating, connection failure, and safety hazards.
- Voltage Requirements: Selecting a terminal block with the proper voltage rating reduces the risk of arcing or insulation breakdown.
- Wire Size: Terminal blocks are designed to accommodate specific wire gauges. For example, this terminal block by Entrelec connects conductors to 4 mm² (12 AWG without an insulated ferrule) within a compact 5.2 mm (0.205 in) spacing.
- Environmental Performance: Terminal blocks can be exposed to extreme temperatures, dust, moisture, chemicals, or vibrations. Therefore, when choosing, consider the temperature range, IP rating (ingress protection), and material durability.
- Scalability: For systems that require expansion or adaptation over time, scalable terminal blocks can future-proof the application with minimal work. Therefore, consider modular, stackable, and pluggable designs that can flexibly meet changing needs over time.
High-Quality Terminal Blocks at Peerless Electronics
Terminal blocks simplify wire installation, offering secure, organized connections in systems, such as control panels, without soldering. They are designed to support easy installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting and allow for streamlined expansion or modifications as needed. Peerless Electronics is a full-service, authorized stocking distributor carrying top-quality terminal blocks for leading manufacturers and suppliers within the military, aerospace, industrial, transportation, and medical sectors.
Peerless Electronics Inc. is certified to AS9100D & ISO9001:2015, meets CMMC compliance requirements, and is a member of ERA and ECIA.
Conveniently shop online for
Terminal Blocks today!
Don’t see what you need in stock? Contact us.
Terminal Block FAQ
Are terminal blocks safe?
Yes, terminal blocks are generally safe when used correctly. They are designed to provide secure, reliable electrical connections, helping to minimize the risks of loose connections, electrical shorts, and fire hazards. Terminal blocks feature insulation to protect against accidental contact and are designed to handle specific current, voltage, and environmental conditions. However, to ensure optimal safety, it’s essential to choose the correct type of terminal block for the application, install it properly, and follow safety standards.
How do I choose the right terminal block for my project?
Several factors must be considered when choosing the most appropriate option for a given application, including current and voltage requirements, wire size, environmental performance, and scalability.
When should you use a terminal block?
Terminal blocks are essential for organizing and connecting multiple wires, making reliable connections, simplifying maintenance and upgrades, reducing the risk of electrical faults, and helping meet compliance and electrical safety standards.












































